Energy Efficiency and Performance in Professional Refrigerators: Impact on Environmental Sustainability and Operational Costs
The concept of food preservation is ancient; throughout history, humans have aimed to maintain the intrinsic properties of food, allowing its use over time. In the modern era, this task is carried out by professional refrigerators, which operate 24/7, 365 days a year, impacting up to 40% of the energy consumption of a professional kitchen.

For this reason, it is crucial to always choose high-quality equipment capable of ensuring a constant and uniform temperature while minimizing energy use to benefit both consumption and the environment.
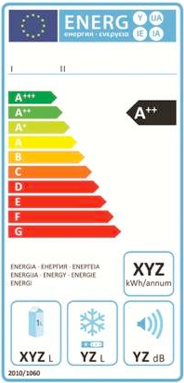
With this goal in mind, the energy class label for professional refrigerators was made legally mandatory starting July 1, 2016. The regulation mandating energy labels for catering equipment originated from the European Union (Regulation 2015/1094/EU), replacing the Italian regulation set by Ceced (the National Association of Domestic and Professional Appliance Manufacturers), which was a private initiative that included some manufacturers and used numerical classes. This highlights the significant attention given to the issue, as well as the competitiveness and technological level of Italian manufacturers, who are considered the best in the world.
The energy label for professional refrigeration appliances has a format very similar to that of labels used for domestic appliances. It includes the energy classification from A (initially) to G, the energy consumption in kWh/year, net capacity in liters, and the climate class (along with the dry-bulb temperature in °C and relative humidity in %). Equipment excluded from the mandatory energy label includes static refrigeration units, combined appliances, chest freezers, and display units used for promoting food sales.