Proofing cabinets or chambers are invaluable for the controlled fermentation of dough created in the kitchens of bakeries, pastry shops, pizzerias, and other businesses that prepare baked goods. They are also used in home kitchens by baking and pastry enthusiasts.
Proofing Cabinets: What They Are and How They Work
A proofing cabinet is a device used in the food industry, as well as in the pharmaceutical and industrial sectors, to create a controlled and stable environment for the fermentation and proofing of food and pharmaceuticals.

How the Proofing Process Works in General
The operation of a proofing cabinet is quite simple: inside the cabinet, a combination of controlled humidity and temperature provides the ideal environment for the growth and fermentation of bacteria, yeast, and molds.
The cabinet is equipped with a ventilation system that ensures proper air circulation and even distribution of humidity and temperature. Some versions of proofing cabinets come with a digital screen or control panel that allows for the setting and monitoring of temperature, humidity, and fermentation time either on-site or remotely.
Proofing cabinets are usually constructed with insulating materials, as well as stainless steel, glass, or plastic, to ensure a sterile and corrosion-resistant environment. Additionally, most proofing chambers are equipped with an automatic disinfection system to prevent bacterial contamination.
How the Dough Proofing Process Works in a Proofing Cabinet
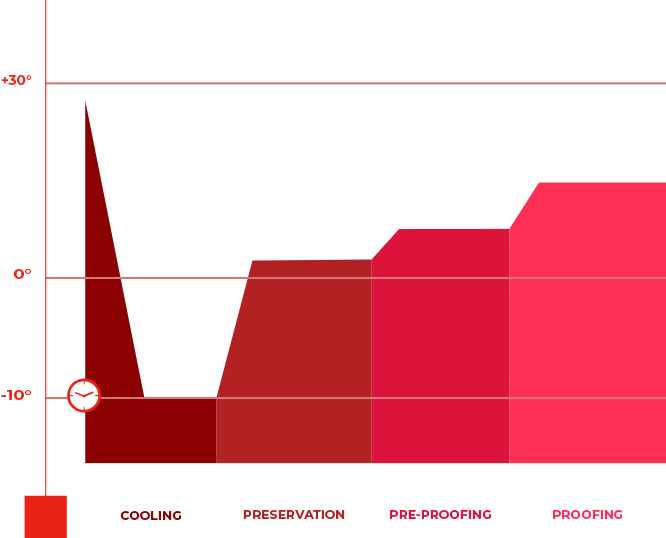
The proofing process of dough is based on the chemical reaction between the enzymes present in the dough and the starch in the flour, which converts sugar into carbon dioxide, responsible for the dough rising. However, proofing at room temperature requires immediate intervention by the operator, often necessitating work at night. To address this issue, proofing cabinets maintain the dough at a constant temperature below 4°C, slowing down the action of the yeast and allowing the start of the process to be scheduled up to 72 hours in advance. Temperature, humidity, and time are precisely controlled in a thermally insulated environment, so fermentation begins only at the set time. This method of slow and controlled proofing ensures greater dough uniformity and prevents the separation between the crust and the interior during baking.
The proofing process generally consists of four phases:
-
Cooling:
This is the blast chilling phase, where the cabinet is brought to very low temperatures (between -10°C and -5°C) to stop the fermentation process of the dough.
-
Preservation:
The cabinet is then adjusted from the blast chilling temperature to the preservation temperature (between -8°C and 2°C) to ensure the dough is preserved for up to 72 hours.
-
Pre-proofing:
The temperature inside the cabinet is gradually increased (between 8°C and 13°C) to slowly and evenly thaw the dough. The duration of this cycle depends on the type of product.
-
Proofing:
This final and crucial phase allows the dough to rise until it is ready to be baked. The operator adjusts the duration, temperature, and humidity based on the product's needs. The precise duration of this phase is crucial for the taste and quality of the final product.
The most common functions of proofing cabinets
To summarize the most common functions of proofing cabinets, regardless of the type, they can be listed as follows:
- Temperature regulation through cooling, heating, and maintenance
- Operation control by reading temperatures from probes such as the evaporator and the suction cell
- Ability to perform complete proofing or resting cycles, following temperature and ventilation characteristics set as needed
- Alternative uses for preservation, thawing, and drying
- Ability to prevent condensation formation on internal surfaces to safeguard operator and product safety
Types of proofing equipment: cabinets and tables for indoor and outdoor use
There are various types of proofing cabinets on the market, all designed to provide a warm and humid environment for dough proofing. The models can vary based on capacity, control options, and safety features.
Smaller models are designed for home use and can hold up to 2-3 trays, while larger commercial models can hold up to 40 trays.
In general, the types of proofing cabinets are temperature-controlled cells that can be used for sourdough proofing, pizza proofing, and other baked goods.
Among temperature-controlled cells, there are cabinet proofing cells and table proofing cells. The choice of use varies depending on production needs and the quantities of products to be proofed.
Cabinet proofing cells
Cabinet proofing cells are usually large and are used for proofing large quantities of baked goods such as bread, pizzas, and pastries. These cells have a controlled ventilation and humidity system that helps maintain the ideal temperature and humidity for proofing.
Table proofing cells
Table proofing cells are smaller and portable, used for proofing smaller quantities of baked goods. These cells typically feature a heating system, temperature and humidity control, and can be placed on a table or flat surface.
Outdoor proofing cabinets
Among proofing cabinets, there are those designed for outdoor use. These cells are weather-resistant and can be used in outdoor environments.
Proofing Cabinets: Advantages
Proofing cabinets offer several advantages as they eliminate the need for nighttime work and allow staff to work at more convenient hours. They enable the storage of large quantities of dough, simplifying production during busy days, and can reduce yeast usage by up to 50%, resulting in significant cost savings. Additionally, the organoleptic properties of the bread are improved due to slower and more uniform proofing achieved through controlled temperature and humidity. Proofing cabinets are also very easy to use. Many models come with intuitive digital controls, allowing bakers and pastry chefs to easily set the desired temperature and humidity.
Proofing Cabinets: Disadvantages
A potential disadvantage of proofing cabinets is that they can be expensive. However, the investment in a proofing cabinet can pay off quickly as it allows for the efficient and consistent production of high-quality baked goods.
Another potential disadvantage is that proofing cabinets require regular maintenance to ensure proper operation, but maintenance is generally simple and can be easily performed by skilled personnel.
Choosing a Proofing Cabinet
When choosing a proofing cabinet for controlled dough proofing, there are several features to consider:
- Size: The cabinet should be large enough to hold all the dough that needs to proof simultaneously while fitting comfortably within the available workspace.
- Temperature and Humidity: The cabinet should be able to maintain constant temperature and humidity levels ideal for dough proofing, typically between 25°C and 30°C with 75% humidity.
- Durability: A high-quality cabinet should be constructed with durable, wear-resistant materials such as wood, stainless steel, or glass to ensure longevity and ease of cleaning.
- Safety Features: The cabinet should have a door lock system and an emergency switch to ensure safety.
- Additional Features: Some cabinets may have additional functionalities such as a timer to regulate proofing time or a cooling system to halt proofing.
- Cost: Consider the available budget and choose a cabinet that offers good value for money.
Once these features are considered, selecting the cabinet that best fits your needs and budget becomes easier.
If you want to purchase proofing cabinets and/or need more information, contact the Cook-In team. We are always available to recommend the most suitable tailored solutions for your needs.



